Time: 2025-11-10 04:16:06 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Low voltage wire and regular (line voltage) wire represent distinct categories in electrical systems, differing primarily in voltage ratings, insulation requirements, applications, and safety considerations. As of November 2025, these distinctions remain governed by standards such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), ensuring appropriate use in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. This guide delineates the key differences to facilitate informed selection and compliance.
Regular wire, often termed line voltage or high voltage wiring, operates at standard household or commercial levels, typically 120V or 240V in North America. Low voltage wire, by contrast, is designed for systems at 50 volts or less (commonly 12V–48V), as defined by NEC for Class 2 and Class 3 circuits.
The following table summarizes the primary distinctions:
| Aspect | Low Voltage Wire | Regular (Line Voltage) Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Typically ≤50V (often 12V–48V) | 120V–240V or higher |
| Insulation Thickness | Thinner and less robust | Thicker for higher dielectric strength |
| Conductor Gauge | Often finer (16–22 AWG) | Thicker (10–14 AWG common) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to materials and ratings |
| Flexibility | More flexible for intricate routing | Less flexible, often in conduits |
| Power Capacity | Limited (e.g., <100VA for Class 2) | High for appliances and lighting |
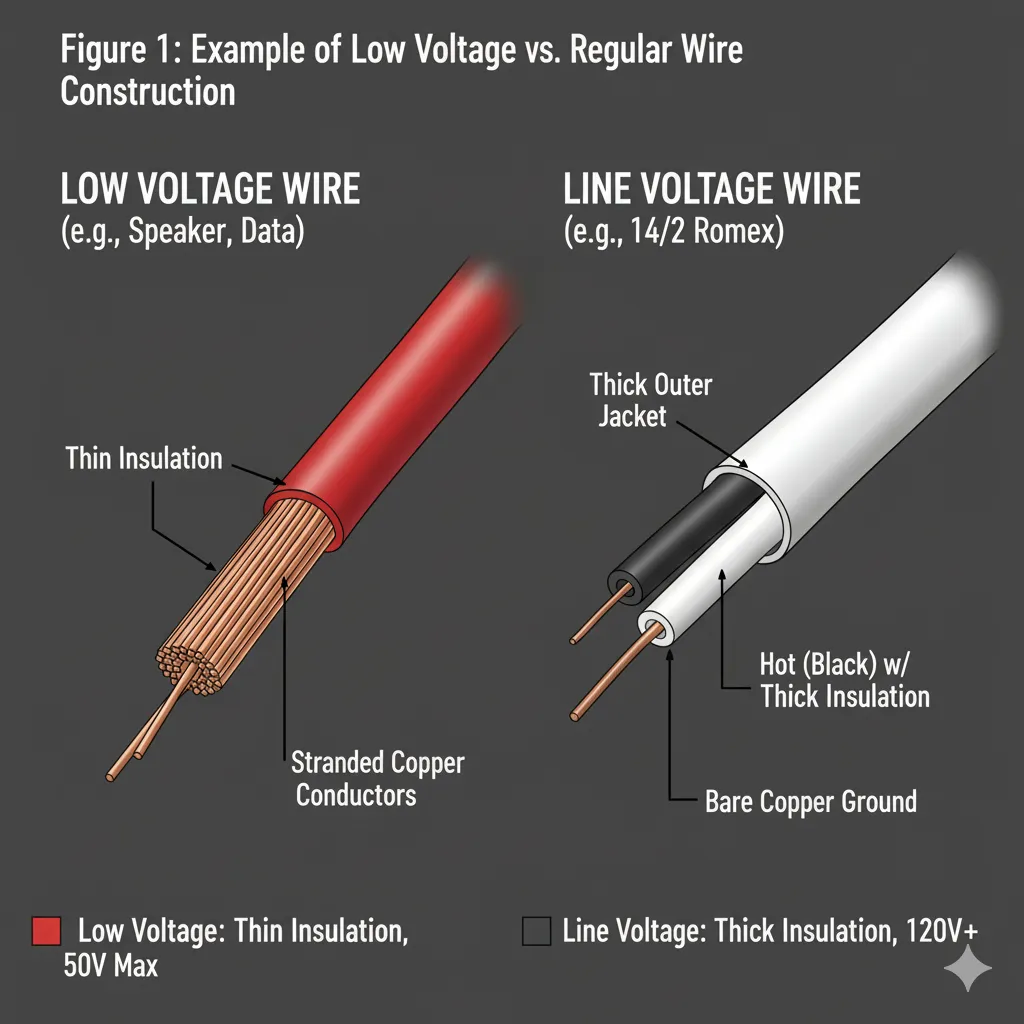
Figure 1: Example of low voltage vs. regular wire construction

Figure 2: Overview of cable shielding and structures in low vs. regular voltage applications
Low voltage wires are employed in signaling and control systems, such as landscape lighting, thermostats, doorbells, security cameras, and audio-visual setups. Regular wires power outlets, lights, and major appliances in building circuits.
Low voltage systems pose minimal shock risk, allowing simpler installation without conduits in many cases. Regular wires require strict adherence to NEC for protection against electrocution and fire, including grounding and overcurrent devices. Mixing the two in enclosures demands insulation rated for the higher voltage.
The fundamental differences between low voltage and regular wire stem from their voltage handling, construction, and intended uses, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Proper identification and application are essential for compliance and performance. Consultation with licensed professionals is advised for specific installations.

CE Certification 450/750v H07VVF Flexible Copper PVC Insulated Ac Cable 3*2.5 Mm

low voltage copper conductor PVC insulation underground BV BVR cable for industr

PVC electric wires are one of the most widely used electrical conductors in resi

H07V-U wire is a flexible, low voltage electrical wire commonly used in industri