What Is RHW Wire and Its Usages?
Time: 2025-05-12 15:44:48
Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
What Is RHW Wire?
RHW wire is a versatile electrical building wire designed for heat and water resistance, making it suitable for demanding indoor and outdoor installations. The acronym RHW stands for Rubber (insulation), Heat-resistant (up to 75°C), and Water-resistant, indicating its ability to withstand high temperatures and wet environments. Typically insulated with cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or flame-retardant ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), RHW wire is rated for 600 volts and is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, including direct burial underground. Its robust insulation aligns with standards like UL 44 and the National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 310, ensuring safety and reliability. RHW wire’s properties make it comparable to other building wires like THHN, XHHW, or TPS cables discussed previously, but its water resistance sets it apart for wet locations.
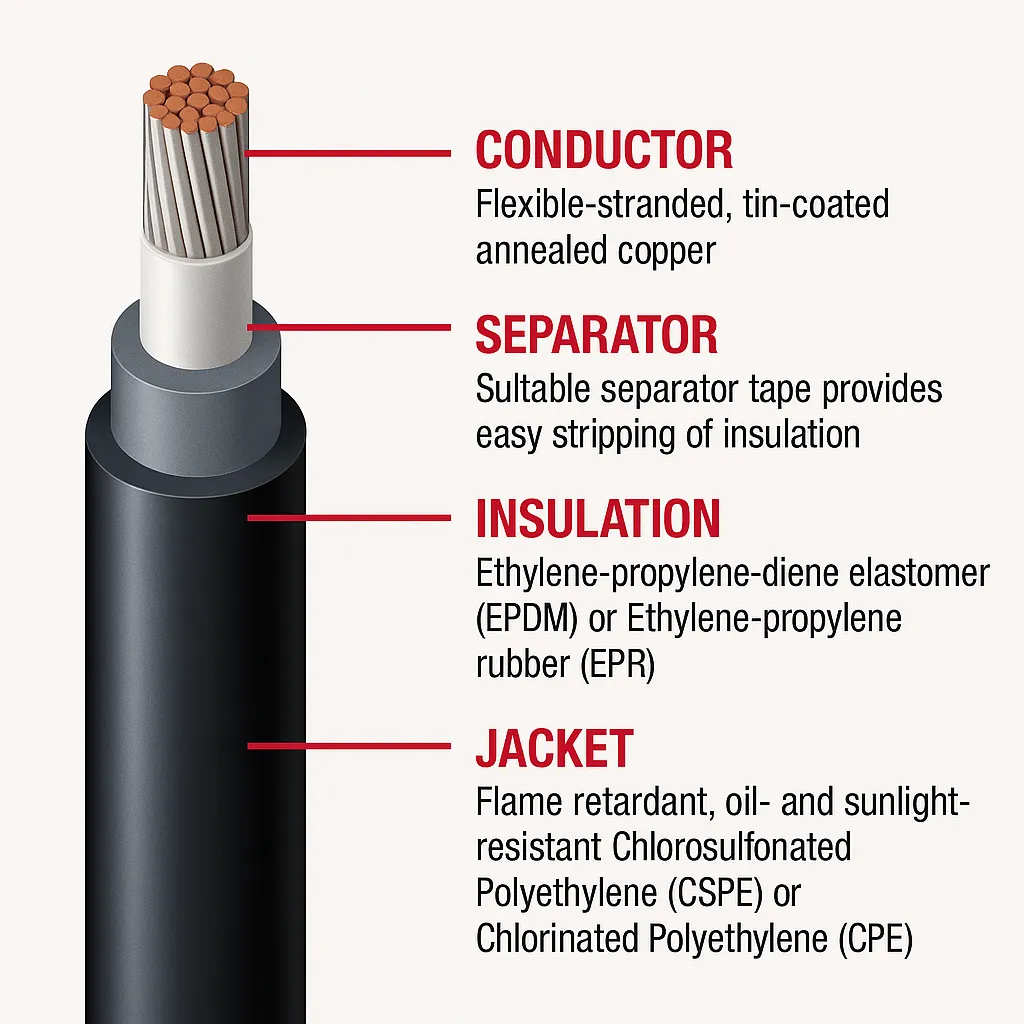
Construction and Properties
RHW wire is engineered for durability in harsh conditions, with a construction that includes:
-
Conductor: Single solid or stranded copper, either bare or tinned, for corrosion resistance and flexibility. Tinned copper, as noted in older installations, enhances longevity in moist environments.
-
Insulation: Typically XLPE or EPR, both thermoset materials offering excellent heat resistance (75°C for RHW, 90°C for RHW-2), water resistance, and chemical resistance to oils and gases. XLPE is lighter and more flame-retardant, akin to MV or submarine cable insulation.
-
Waterproofing: Some RHW cables include water-resistant tape or expansion strips between the insulation and outer layers, creating a longitudinal barrier against moisture penetration, ideal for underground use.
-
Outer Sheath: Often absent, as the insulation itself provides protection, but some designs include a thin protective layer for added abrasion resistance.
Key properties include a 600V rating, sunlight resistance, and suitability for wet or dry locations. RHW-2’s enhanced insulation supports higher temperatures (90°C), making it more versatile. This construction mirrors the durability of LSOH or PUR cables but prioritizes water resistance, unlike RHH, which lacks the “W” designation.
Types of RHW Wire
RHW wire is categorized by temperature rating and dual ratings for specific applications:
-
RHW: Standard RHW wire, rated for 75°C in wet or dry locations, insulated with XLPE or EPR. Suitable for general-purpose wiring in moist environments.
-
RHW-2: An upgraded version rated for 90°C in wet or dry conditions, often dual-rated as USE-2 (Underground Service Entrance) for direct burial. Commonly used in solar or industrial applications.
-
RHH/RHW-2/USE-2: Dual- or triple-rated cables combining RHH (90°C, dry locations only), RHW-2, and USE-2 properties. These offer maximum versatility for power distribution, lighting, and photovoltaic systems.
Sizes range from 14 AWG to 4/0 AWG, with common sizes like 8 AWG, 10 AWG, and 12 AWG for residential or commercial use. Stranded conductors enhance flexibility, similar to multi-conductor or TPI cables, while solid conductors suit fixed installations.
Applications of RHW Wire
RHW wire’s heat and water resistance make it ideal for a wide range of applications:
-
Residential Wiring: Used for service feeders, branch circuits, and underground power supply for outdoor lighting or landscape systems, leveraging its direct burial capability.
-
Commercial Buildings: Powers distribution systems in offices, retail stores, and small facilities, suitable for conduits or raceways in wet locations.
-
Industrial Environments: Connects equipment, control lines, and diesel generators in factories or warehouses, where resistance to high temperatures, moisture, oils, and gases is critical.
-
Underground and Overhead Installations: Direct burial for underground trenches or aerial installations (when supported by a messenger), ideal for pipe and trench wiring or outdoor power systems.
-
Renewable Energy: RHW-2/USE-2 is used in photovoltaic systems as solar wire, connecting wind towers or solar panels to boosters, due to its sunlight, heat, and moisture resistance.
-
Cathodic Protection: Serves as a sacrificial wire in corrosion prevention systems, benefiting from XLPE’s toughness, similar to submarine cable durability.
These applications highlight RHW’s versatility, akin to THHN or XHHW in building wiring or TPS cables in residential settings, but with superior water resistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
RHW wire offers several benefits but also has limitations:
-
Advantages:
-
Heat and Water Resistance: Operates reliably up to 75°C (90°C for RHW-2) in wet or dry conditions, ideal for underground or humid environments.
-
Direct Burial Capability: Suitable for underground installations without additional conduit, reducing installation costs.
-
Chemical Resistance: Resists oils, gases, and abrasion, enhancing durability in industrial settings.
-
Versatility: Dual ratings (e.g., RHH/RHW-2/USE-2) allow use in diverse applications, from solar to building wiring.
-
Compliance: Meets UL 44, UL 854, and NEC Article 310 standards, ensuring safety and reliability.
-
Disadvantages:
-
Lower Temperature Rating: RHW (75°C) is less heat-resistant than RHH or XHHW-2 (90°C), limiting use in high-temperature dry environments.
-
Cost: XLPE or EPR insulation is more expensive than PVC-based insulation like THHN or TPS, increasing material costs.
-
Weight: Heavier than XHHW due to thicker insulation, potentially complicating large-scale installations.
-
Flexibility: Less flexible than stranded TPI or TPE cables, requiring careful handling in tight spaces.
These trade-offs echo discussions of LSOH vs. PVC or Teflon’s specialized applications, balancing cost and performance.
RHW vs. RHH vs. USE-2 Comparison Table
RHW, RHH, and USE-2 are related building wires with overlapping applications. The table below compares their key attributes:
|
Feature
|
RHW
|
RHH
|
USE-2
|
|
Insulation
|
XLPE or EPR
|
XLPE or EPR
|
XLPE
|
|
Temperature Rating
|
75°C (wet/dry)
|
90°C (dry only)
|
90°C (wet/dry)
|
|
Water Resistance
|
Yes
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Voltage Rating
|
600V
|
600V
|
600V
|
|
Direct Burial
|
Yes
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Applications
|
Building wiring, underground
|
High-temp dry locations
|
Solar, underground service
|
|
Standards
|
UL 44, NEC Article 310
|
UL 44, NEC Article 310
|
UL 854, NEC Article 310
|
Note: RHW-2 is often dual-rated as USE-2 or RHH, enhancing its versatility. Verify specifications with NEC or local codes.
Tips for Choosing RHW Wire
Selecting RHW wire requires careful consideration of project needs:
-
Assess Environmental Conditions: Use RHW or RHW-2 for wet locations or direct burial; opt for RHH in high-temperature dry environments.
-
Match Temperature Requirements: Choose RHW-2 (90°C) for applications exceeding 75°C, such as solar or industrial systems.
-
Select Conductor Size: Use 12 AWG for lighting (15-20A), 10 AWG for outlets (20-30A), or larger sizes like 8 AWG for high-current feeders, ensuring compliance with NEC ampacity tables.
-
Consider Installation Type: Opt for stranded RHW for flexibility in conduits or tight spaces, or solid for fixed direct burial setups, similar to TPS or multi-conductor cables.
-
Verify Standards: Ensure compliance with UL 44, UL 854, or NEC Article 310, especially for underground or commercial installations.
-
Evaluate Cost vs. Performance: RHW may be costlier than THHN but is justified for wet environments; compare with XHHW for lighter alternatives.
-
Consult Professionals: Engage licensed electricians to validate wire selection and installation, ensuring adherence to local codes like AS/NZS 3000 or NEC.
These steps ensure optimal performance, similar to selecting submarine or thermoplastic insulated cables.
Conclusion
RHW wire is a robust, multi-purpose building wire designed for heat and water resistance, making it ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications, including direct burial and renewable energy systems. With XLPE or EPR insulation, it supports 600V systems and operates reliably in wet or dry conditions up to 75°C (90°C for RHW-2). Available in sizes like 8 AWG to 4/0 AWG, RHW’s versatility is enhanced by dual ratings like RHH/RHW-2/USE-2, catering to diverse needs from underground feeders to solar installations. While costlier and less flexible than alternatives like THHN or TPS, its durability and compliance with UL and NEC standards ensure safety and longevity. By assessing environmental conditions, selecting appropriate sizes, and consulting professionals, users can leverage RHW wire’s strengths for reliable electrical systems, building on the adaptability of cables like XHHW or multi-conductor designs discussed previously.
