DLO vs. Welding Cable: Key Differences and Applications
Time: 2025-05-18 14:03:27
Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Overview of DLO and Welding Cables
Diesel Locomotive (DLO) and welding cables are flexible, high-current cables designed for demanding applications, often confused due to their similar construction and appearance. Both feature stranded copper conductors and durable jackets, but they differ in design, ratings, and intended uses. DLO cables, originally developed for locomotive wiring, are now used in industrial and heavy-duty power applications, while welding cables are primarily designed for welding equipment. Understanding their differences is critical for selecting the appropriate cable, as discussed in prior articles on AWG, automotive wires, solar cables, and cable jackets.
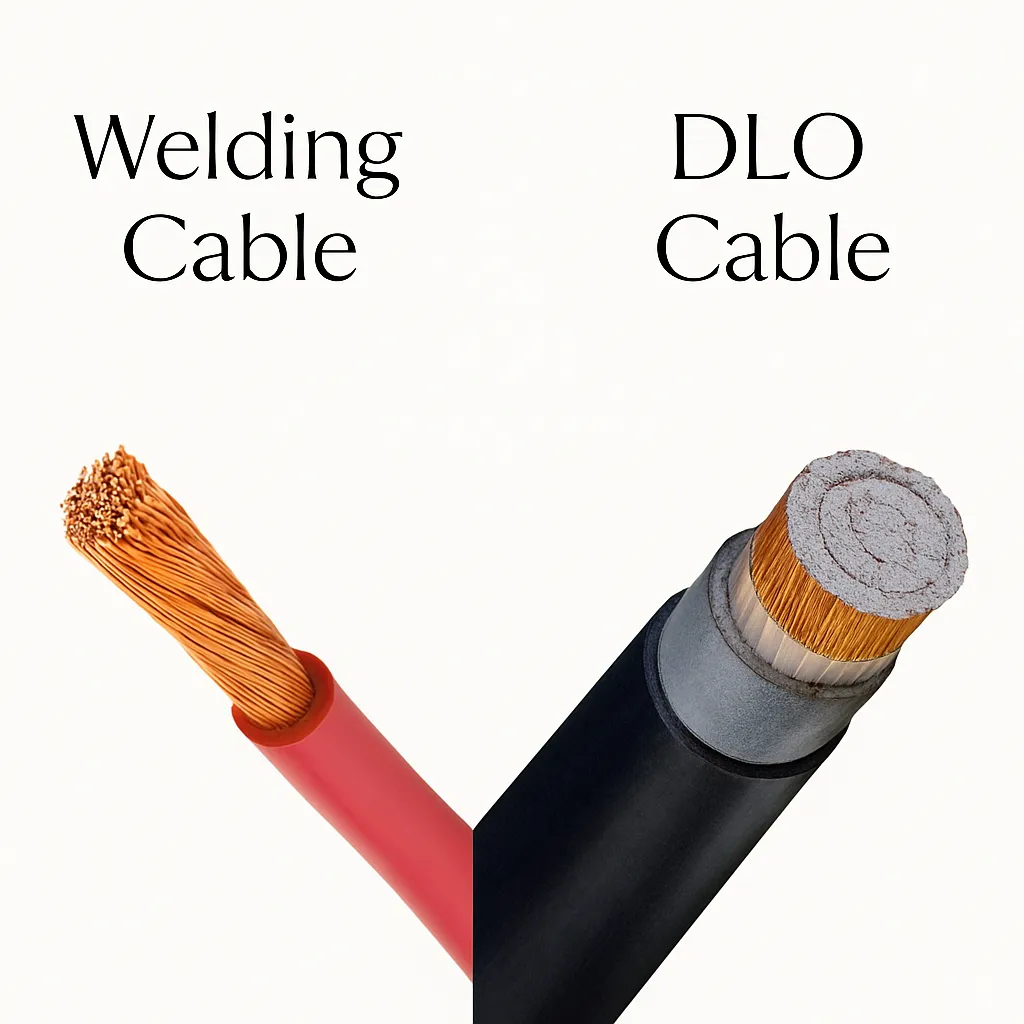
Key Differences Between DLO and Welding Cables
DLO and welding cables differ in construction, electrical ratings, and intended uses, impacting their performance and interchangeability:
-
Conductor Material: DLO cables use tinned copper conductors, enhancing corrosion resistance for harsh environments like mining or marine settings. Welding cables typically use bare copper, which is less resistant to corrosion but sufficient for welding applications.
-
Insulation and Jacket: DLO cables feature thicker insulation, such as ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), and a robust jacket, like chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), rated for 2000V and temperatures up to 90°C in wet or dry conditions, offering superior durability. Welding cables have thinner insulation, typically EPDM or Neoprene, rated for 600V and up to 105°C, optimized for flexibility but less durable.
-
Voltage and Current Ratings: DLO cables are rated for 2000V, suitable for high-voltage industrial applications, and can handle higher continuous currents, such as 127A for 2 AWG at 90°C. Welding cables, rated for 600V, are designed for intermittent high-current welding, such as 190A for 2 AWG, with lower performance under sustained loads.
-
Installation Suitability: DLO cables are suitable for permanent wiring in conduits or raceways, making them versatile for industrial setups. Welding cables are typically limited to welding or temporary applications, requiring specific ratings for other uses.
-
Flexibility: Both cables are highly flexible due to fine-stranded conductors, but welding cables are slightly more flexible, ideal for frequent repositioning in welding. DLO cables, while flexible, are heavier and stiffer due to thicker insulation, suited for semi-permanent setups.
These differences highlight that while DLO can sometimes substitute for welding cable in high-current applications, the reverse is rarely true due to welding cable’s lower ratings and installation limitations.
Advantages of DLO and Welding Cables
Both cable types offer distinct benefits tailored to their applications:
-
DLO Cable Advantages:
-
Durability: Tinned conductors and robust EPR/CPE insulation resist oils, chemicals, abrasion, and extreme temperatures from -40°C to 90°C, ideal for harsh environments, similar to H07RN-F cables.
-
High Voltage Rating: 2000V rating supports heavy-duty power supply, surpassing welding cables and aligning with medium-voltage cable capabilities.
-
Versatility: Suitable for permanent wiring, increasing applicability in industrial settings.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Tinned copper enhances longevity in corrosive settings, akin to marine or solar cables.
-
Welding Cable Advantages:
-
Flexibility: Thinner insulation and fine strands provide superior flexibility, ideal for welding and temporary setups, similar to trailing cables.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Lower cost due to simpler construction, suitable for budget-conscious welding applications.
-
Cold Weather Performance: Flexible insulation, such as EPDM, performs well in cold temperatures, unlike some automotive cables.
-
Ease of Use: Lightweight and easy to maneuver, enhancing usability in dynamic welding environments.
These advantages reflect their specialized roles, with DLO excelling in durability and welding cables in flexibility.
Applications of DLO and Welding Cables
DLO and welding cables serve distinct yet overlapping applications, similar to 6 AWG, automotive, and solar cables:
-
DLO Cable Applications:
-
Industrial Power Supply: Powers heavy machinery, motors, and generators in mining, oil and gas, and manufacturing, leveraging 2000V rating.
-
Temporary Power: Used in generator backups with cam-locks for events or construction sites.
-
Locomotive Wiring: Originally designed for diesel locomotives, now used in rail and transit systems.
-
Marine and Mining: Tinned conductors suit corrosive and wet environments, similar to submarine cables.
-
Welding Cable Applications:
-
Welding Equipment: Connects welding machines to electrodes, handling intermittent high currents, primary use case.
-
Portable Power: Used in low-voltage temporary setups like construction sites, where flexibility is key.
-
Automotive: Powers high-current battery connections or audio systems, similar to automotive wires.
-
Stage Lighting: Occasionally used for flexible, temporary lighting setups, though less common than stage cables.
While DLO cables are suited for heavy-duty, permanent, or semi-permanent installations, welding cables excel in flexible, temporary, or welding-specific tasks.
Comparison of DLO and Welding Cables
The table below compares DLO and welding cables, highlighting their properties:
|
Feature
|
DLO Cable
|
Welding Cable
|
|
Conductor
|
Tinned copper, fine-stranded
|
Bare copper, fine-stranded
|
|
Insulation/Jacket
|
EPR/CPE, thick
|
EPDM/Neoprene, thin
|
|
Voltage Rating
|
2000V
|
600V
|
|
Temperature Range
|
-40°C to 90°C (wet/dry)
|
-50°C to 105°C
|
|
Ampacity (2 AWG, 90°C)
|
127A (continuous)
|
190A (intermittent)
|
|
Flexibility
|
High, but stiffer than welding
|
Very high, lightweight
|
|
Installation Suitability
|
Suitable for conduit, permanent wiring
|
Limited to welding, temporary uses
|
|
Typical Applications
|
Industrial, locomotive, marine
|
Welding, portable power, automotive
|
Tips for Selecting Between DLO and Welding Cables
Choosing between DLO and welding cables ensures performance and safety:
-
Assess Voltage and Current Needs: Select DLO for high-voltage, up to 2000V, or continuous high-current applications, such as 127A for 2 AWG; use welding cable for low-voltage, 600V, or intermittent high-current tasks, like welding at 190A. Refer to ampacity tables, as discussed in AWG articles.
-
Consider Environmental Conditions: Choose DLO for corrosive, wet, or harsh environments due to tinned conductors and robust jackets, similar to solar or H07RN-F cables; use welding cable for less demanding settings.
-
Evaluate Flexibility Requirements: Opt for welding cable in dynamic applications requiring frequent movement, like welding or temporary setups; use DLO for semi-permanent installations, akin to trailing cables.
-
Verify Installation Needs: Ensure DLO cables are suitable for conduit or permanent wiring in industrial setups; confirm welding cables are appropriate for non-welding uses if needed.
-
Balance Cost and Durability: Welding cables are cheaper but less durable; DLO cables cost more but offer longevity, ideal for industrial applications, similar to medium-voltage or solar cables.
-
Consult Professionals: Engage electricians to verify sizing and installation, ensuring reliability, as with automotive or household cables.
These steps align with selecting reliable cables like TR-XLPE, LSOH, or 6 AWG.
Conclusion
DLO and welding cables, while similar in flexibility and high-current capabilities, serve distinct purposes due to differences in conductor material, insulation, voltage ratings, and installation suitability. DLO cables, with tinned copper, robust EPR/CPE jackets, and 2000V ratings, excel in heavy-duty, permanent, or harsh-environment applications like industrial power, locomotive wiring, and marine systems. Welding cables, with bare copper and thinner insulation, are ideal for flexible, low-voltage, or temporary setups like welding and portable power. By evaluating electrical, environmental, and installation requirements, users can select the appropriate cable, ensuring safety and efficiency. Professional consultation further enhances reliability, building on discussions of AWG, automotive wires, solar cables, and cable jackets.
