Single-Core Wires: Applications and Functionality
Time: 2025-05-21 15:58:49
Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Introduction to Single-Core Wires
A single-core wire, also referred to as a single-conductor wire, consists of a single conductive core, typically made of copper or aluminum, surrounded by an insulating layer and, in some cases, an outer protective sheath. These wires are designed to transmit electrical power or signals in a variety of applications, offering simplicity and reliability for specific electrical and control systems. Single-core wires are fundamental components in electrical installations, valued for their straightforward design and versatility in both low- and high-voltage applications.
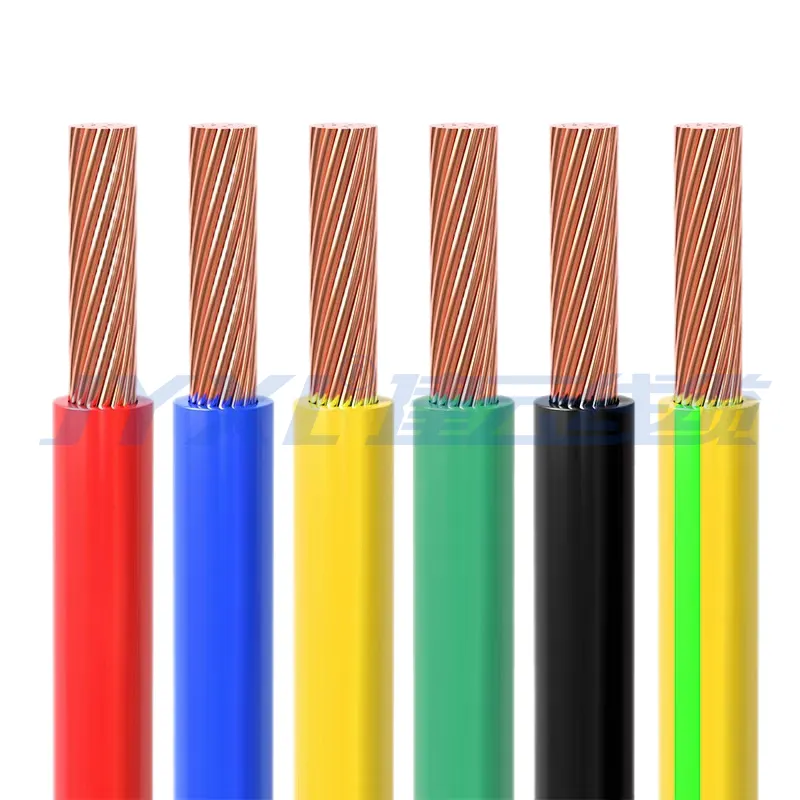
Design and Construction
Single-core wires are engineered to meet specific electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements. Their key components include:
-
Conductor: The core is typically made of copper for high conductivity or aluminum for cost-effective and lightweight applications. The conductor may be solid (a single piece of metal) or stranded (multiple thin strands twisted together) to enhance flexibility.
-
Insulation: The conductor is coated with an insulating material, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), to prevent unwanted electrical contact and ensure safety.
-
Outer Sheath (Optional): In some applications, an additional protective jacket, made of materials like PVC or low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH), shields the wire from moisture, chemicals, or mechanical damage.
-
Armor (Optional): For demanding environments, such as underground or industrial settings, a metallic armor layer may be added for enhanced durability.
Primary Applications of Single-Core Wires
Single-core wires are used in a wide range of applications where a single electrical conductor is sufficient for power or signal transmission. Their main applications include:
-
Power Distribution: Single-core wires are used in single-phase or three-phase power systems, often as individual phase, neutral, or ground conductors in residential, commercial, or industrial installations.
-
Building Wiring: Commonly employed in electrical wiring for homes, offices, and public buildings to connect circuits for lighting, outlets, and appliances.
-
Grounding and Earthing: Single-core wires, often uninsulated or with green/yellow insulation, are used as grounding conductors to ensure electrical safety by providing a path for fault currents.
-
High-Voltage Transmission: In utility networks, single-core wires are used in high-voltage transmission lines, often as part of overhead or underground systems, to transmit power over long distances.
-
Control and Signal Circuits: In control systems, single-core wires transmit signals for automation, instrumentation, or communication equipment, such as in industrial sensors or telecommunications.
-
Automotive and Marine Applications: Single-core wires power low-voltage systems, such as lighting or ignition circuits, in vehicles and boats, with designs suited to withstand vibration and environmental exposure.
Advantages of Single-Core Wires
Single-core wires offer several benefits that make them suitable for their applications:
-
Simplicity: Their single-conductor design is straightforward, making them easy to manufacture, install, and maintain.
-
High Conductivity: Solid or stranded conductors provide efficient power or signal transmission, especially in high-current applications.
-
Durability: Robust insulation and optional sheathing ensure reliable performance in various environments, including indoor, outdoor, or industrial settings.
-
Flexibility in Use: Available in a range of sizes, materials, and insulation types, single-core wires can be tailored to specific voltage, current, or environmental requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
While single-core wires are effective, certain challenges must be addressed:
-
Limited Functionality: Single-core wires are designed for single-circuit applications and cannot support complex systems requiring multiple phases or signals without additional wires.
-
Environmental Exposure: Wires exposed to moisture, extreme temperatures, or chemicals require specialized insulation or sheathing to prevent degradation.
-
Mechanical Stress: Solid-core wires may be less flexible than stranded wires, making them susceptible to damage from bending or vibration in dynamic applications.
To address these challenges, single-core wires are designed to comply with industry standards, such as those set by organizations like the Association of Edison Illuminating Companies (AEIC), ensuring performance, safety, and compatibility in utility and industrial applications.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are critical for the performance of single-core wires:
-
Installation: Wires must be installed with appropriate support, avoiding sharp bends or excessive tension, particularly in aerial or underground setups. Correct termination to equipment or junction boxes ensures reliable connections.
-
Termination and Jointing: Accurate termination, using proper connectors or terminals, prevents loose connections or electrical faults.
-
Maintenance: Regular inspections for insulation wear, corrosion, or physical damage help prevent failures. Testing for continuity and insulation resistance can identify potential issues early.
Future Trends
As electrical systems evolve, single-core wires are adapting to meet new demands:
-
Smart Systems Integration: Single-core wires are being optimized for low-voltage control circuits in smart homes, IoT devices, and automation systems.
-
Sustainable Materials: Eco-friendly insulation and conductor materials are being developed to reduce environmental impact.
-
High-Efficiency Conductors: Advances in conductor materials, such as high-conductivity alloys, are improving performance in high-voltage and long-distance applications.
-
Compact Designs: Innovations in insulation technology are enabling thinner, more flexible single-core wires for space-constrained applications.
Conclusion
Single-core wires are fundamental components in electrical and control systems, offering a simple and reliable solution for power and signal transmission. Their versatility, durability, and efficiency make them essential in applications ranging from building wiring to high-voltage transmission and control circuits. As technology advances, single-core wires will continue to support the evolving needs of modern electrical infrastructure, contributing to safe, efficient, and sustainable systems.
