Time: 2025-03-12 14:28:45 Source: Henan Province Jianyun Cable Co., Ltd.
Medical equipment cables are a critical component in modern healthcare, ensuring reliable power transmission, data communication, and patient monitoring. Unlike standard industrial cables, medical cables must meet strict regulatory and safety standards, as they operate in environments requiring biocompatibility, flexibility, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance.
This article provides an overview of medical equipment cables, including:
By analyzing these aspects, we aim to understand how the industry can improve the safety, performance, and standardization of medical cables.
Medical equipment cables are custom-designed for specific applications, with different requirements for insulation, shielding, and durability. They can be classified into the following categories:
| Type | Application | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Cables | MRI, CT scanners, ultrasound devices | EMI shielding, low-noise transmission |
| Therapeutic Cables | Surgical tools, laser treatment devices | Heat resistance, flexibility |
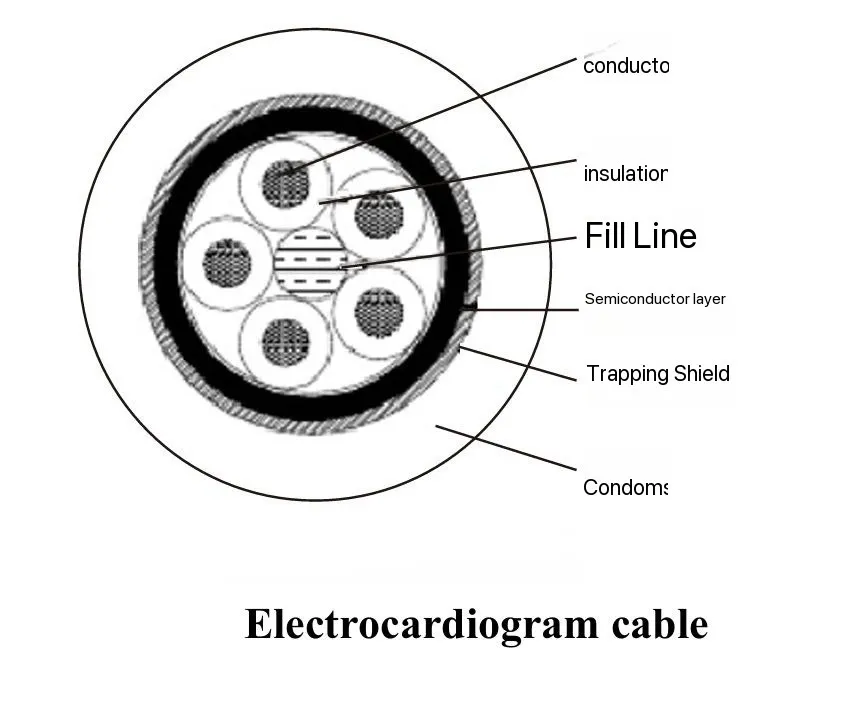
| Patient Monitoring Cables | ECG, blood pressure monitors | Biocompatibility, soft insulation |
| Laboratory Equipment Cables | Biochemical analyzers, automated blood testing | Chemical resistance, precise data transmission |
➡ Key Insight: Each category of cable has distinct material and structural requirements, making standardization complex.
Medical cables must be manufactured with materials that meet strict regulatory and safety requirements.
Conductors must provide high electrical conductivity and resistance to oxidation. Common materials include:
➡ Challenge: Conductors must be flexible enough to withstand repeated bending while maintaining low electrical resistance.
Insulation protects conductors from electrical leakage, mechanical damage, and chemical exposure.
| Material | Properties | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Cost-effective, flexible | General medical wiring |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | High flexibility, wear-resistant | Patient monitoring cables |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon) | High heat and chemical resistance | Surgical instruments |
➡ Challenge: Insulation must prevent interference while ensuring biocompatibility.
Medical cables require shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI), especially in sensitive monitoring equipment.
| Shielding Type | Advantages | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Braided Copper Shield | Best EMI protection | MRI and CT scanners |
| Aluminum Foil Shield | Lightweight, cost-effective | General data cables |
| Conductive Polymer Shield | Flexible, resistant to mechanical wear | Patient monitoring devices |
➡ Challenge: Shielding must balance flexibility, EMI protection, and durability.
The outer sheath protects the cable from physical damage, sterilization chemicals, and mechanical stress.
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Silicone Rubber | High flexibility, resistant to sterilization |
| Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Biocompatible, chemical resistant |
| Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP) | Heat-resistant, low friction |
➡ Challenge: Cables must remain durable under sterilization cycles (e.g., autoclave, alcohol wipes).
To ensure reliability, medical cables undergo strict performance testing based on international safety standards.
Medical cables must pass electrical, mechanical, and environmental tests:
| Test | Purpose | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Withstand Test | Ensures insulation integrity | ANSI/UL 2556 |
| Flexibility & Bend Test | Measures durability under bending cycles | ISO 6722 |
| EMI Shielding Test | Prevents signal interference | IEC 60601-1 |
| Biocompatibility Test | Ensures no harmful effects on the human body | ISO 10993 |
➡ Key Finding: Many existing standards do not fully address customization needs, making harmonized global regulations necessary.
With the growth of wearable medical devices, AI-driven diagnostics, and 5G healthcare systems, the demand for more advanced medical cables is increasing.
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Miniaturization of Medical Cables | Enables smaller, more portable medical devices |
| Smart Cables with Embedded Sensors | Real-time health monitoring & diagnostics |
| High-Frequency Data Transmission Cables | Supports AI-driven medical imaging |
➡ Conclusion: The future of medical cables lies in innovation, miniaturization, and global standardization.
Medical equipment cables differ significantly from standard industrial cables due to their strict safety requirements, unique material composition, and high customization levels.
✔ Material selection plays a crucial role in ensuring performance, safety, and durability.
✔ Testing and certification challenges highlight the need for global standardization.
✔ Future advancements in smart cables and miniaturization will drive innovation in medical devices.
As medical technology continues to evolve, ensuring high-quality, safe, and standardized cables will remain a top priority for the healthcare industry.